What are
the default configuration files that are used in Hadoop
|
As of
0.20 release, Hadoop supported the following read-only default configurations
-
src/core/core-default.xml
-
src/hdfs/hdfs-default.xml
-
src/mapred/mapred-default.xml
|
How will
you make changes to the default configuration files
|
Hadoop
does not recommends changing the default configuration files, instead it
recommends making all site specific changes in the following files
-
conf/core-site.xml
-
conf/hdfs-site.xml
-
conf/mapred-site.xml
Unless
explicitly turned off, Hadoop by default specifies two resources, loaded
in-order from the classpath:
-
core-default.xml : Read-only defaults for hadoop.
-
core-site.xml: Site-specific configuration for a given hadoop installation.
Hence if
same configuration is defined in file core-default.xml and src/core/core-default.xml then
the values in file core-default.xml (same is true for other 2
file pairs) is used. |
Tuesday, December 4, 2012
Hadoop Interview Questions
Monday, December 3, 2012
Hadoop Interview Question
- What is Hadoop? Brief about the components of Hadoop.
- What are the Hadoop daemon processes tell the components of Hadoop and functionality?
- Tell steps for configuring Hadoop?
- What is architecture of HDFS and flow?
- Can we have more than one configuration setting for Hadoop cluster how can you switch between these configurations?
- What will be your troubleshooting approach in Hadoop?
- What are the exceptions you have come through while working on Hadoop, what was your approach for getting rid of those exceptions or errors?
Thursday, October 4, 2012
100 C Questions and Answers
Tuesday, September 18, 2012
Demystifying Hadoop concepts Series: Safe mode
What is is safe mode of hadoop, may time we come across this exception “ org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException: org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.SafeModeException” or some other exceptions Which contains safe mode in it ![]() .
.
First let me tell what Safe mode is in context to Hadoop : as we all know Name node contains fsimage (metadata) of the data present on the cluster, which can be large or small based on the size of the cluster and the size of date present on the cluster, so when the name node starts it loads this fsimage and the edit logs from the disk in the Primary memory RAM for fast processing, and after loading it waits for data nodes to report about the present on those data nodes, so during this process that is loading the fsimage and edit logs and waiting for data nodes to report about the data block in safe mode, which is a read only mode for name node this is done to maintain the consistency of the data present, this is just like saying “ i will not receive any thing till i know what i already have”. And during this period no modification to the file blocks are allowed as to maintain the correctness of the data.
How long safemode exist :
Generally name node automatically comes out of safe mode in 30 seconds if all data present are consistent according the fsimage and the editlogs.
Related commands :
Put Namenode in Safemode: bin/hadoop dfsadmin –safemode
Leave Safemode : bin/hadoop dfsadmin -safemode leave
What to do if you encounter this exception :
First, wait a minute or two and then retry your command. If you just started your cluster, it's possible that it isn't fully initialized yet. If waiting a few minutes didn't help and you still get a "safe mode" error, check your logs to see if any of your data nodes didn't start correctly (either they have Java exceptions in their logs or they have messages stating that they are unable to contact some other node in your cluster). If this is the case you need to resolve the configuration issue (or possibly pick some new nodes) before you can continue.
Tuesday, June 5, 2012
What do you mean by Object Slicing?
{
public int i;
};
class DerivedClass : public BaseClass
{
public int j;
};
int main()
{
BaseClass ObjectOfB;
DerivedClass ObjectOfD;
ObjectOfB = ObjectOfD;
//Here ObjectOfD contains both i and j.
//But only i is copied to ObjectOfB.
}
What is difference between overloading and overriding?
Having same name methods with different parameters is called overloading, while having same name and parameter functions in base and drive class called overriding. |
Tuesday, May 1, 2012
How to : Variable Prameters in c# function.
We can use “params” to enable a method to accept variable number of parameters. For using this we can send comma parameter list as somefunction(1,2,3,1,3,4) to the method.
Sunday, April 22, 2012
Which interface needs to be implemented to create Mapper and Reducer for the Hadoop?
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper ( and ) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer
Thursday, April 19, 2012
how to calculate median in Hive
percentile(BIGINT col, p)
and set p to be 0.5
Will calculate median :)
Tuesday, April 17, 2012
What is the difference between HDFS and NAS ?
- The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware. It has many similarities with existing distributed file systems. However, the differences from other distributed file systems are significant. Following are differences between HDFS and NAS
- In HDFS Data Blocks are distributed across local drives of all machines in a cluster. Whereas in NAS data is stored on dedicated hardware.
- HDFS is designed to work with Map Reduce System, since computation are moved to data. NAS is not suitable for Map Reduce since data is stored separately from the computations.
- HDFS runs on a cluster of machines and provides redundancy using replication protocol. Whereas NAS is provided by a single machine therefore does not provide data redundancy.
What is a Job Tracker in Hadoop? How many instances of Job Tracker run on a Hadoop Cluster?
- Job Tracker is the daemon service for submitting and tracking Map Reduce jobs in Hadoop. There is only One Job Tracker process run on any hadoop cluster. Job Tracker runs on its own JVM process. In a typical production cluster its run on a separate machine. Each slave node is configured with job tracker node location. The Job Tracker is single point of failure for the Hadoop Map Reduce service. If it goes down, all running jobs are halted. Job Tracker in Hadoop performs following actions(from Hadoop Wiki:)
- Client applications submit jobs to the Job tracker.
- The JobTracker talks to the NameNode to determine the location of the data
- The JobTracker locates TaskTracker nodes with available slots at or near the data
- The JobTracker submits the work to the chosen TaskTracker nodes.
- The TaskTracker nodes are monitored. If they do not submit heartbeat signals often enough, they are deemed to have failed and the work is scheduled on a different TaskTracker.
- A TaskTracker will notify the JobTracker when a task fails. The JobTracker decides what to do then: it may resubmit the job elsewhere, it may mark that specific record as something to avoid, and it may may even blacklist the TaskTracker as unreliable.
- When the work is completed, the JobTracker updates its status.
- Client applications can poll the JobTracker for information.
What is compute and Storage nodes?
Compute Node: This is the computer or machine where your actual business logic will be executed.
Storage Node: This is the computer or machine where your file system reside to store the processing data.
In most of the cases compute node and storage node would be the same machine.
What is Map Reduce ?
Map reduce is an algorithm or concept to process Huge amount of data in a faster way. As per its name you can divide it Map and Reduce.
- The main Map Reduce job usually splits the input data-set into independent chunks. (Big data sets in the multiple small datasets)
- Map Task: will process these chunks in a completely parallel manner (One node can process one or more chunks).
- The framework sorts the outputs of the maps.
- Reduce Task : And the above output will be the input for the reduce tasks, produces the final result.
Your business logic would be written in the Mapped Task and Reduced Task.
Typically both the input and the output of the job are stored in a file-system (Not database). The framework takes care of scheduling tasks, monitoring them and re-executes the failed tasks.
What is Hadoop framework
Hadoop is a open source framework which is written in java by apache software foundation. This framework is used to write software application which requires to process vast amount of data (It could handle multi TB of data). It works in-parallel on large clusters which could have 1000 of computers (Nodes) on the clusters. It also process data very reliably and fault-tolerant manner. See the below image how does it looks.
Thursday, April 12, 2012
What is Strongly Typed.
- This means that the data type, is predefined, which prevents programmers to invent and add new data type, to enforce this the language compiler comes in play, it takes care of checking the typed at the compile time only.
- In more clear way we can say that the programming language is strongly typed if it does not allows to define a variable with a data type, we can take and example of c, in which whenever we declare a variable we need to specify its data type also e.g.: int a, char b, but some other languages are loosely typed as we can just give var a, or $var which can hold any data type assigned.
- One more explanation is that in strongly typed the data type is checked at compile time but in loosely typed this done at runtime.
Why Generic type???

- It helps us to separate logic from data type, means no matter what type of data type we are passing to method, will be handled using the same function.
- In other way, we can avoid polymorphism, means only one function can handle different data type rather than defining many function with different kind of data type.
- Generic type invocation as being similar to an ordinary method invocation, but instead of passing an argument to a method, you're passing a type argument
Sunday, April 1, 2012
What is the difference between const and static readonly?
The difference is that the value of a readonly field is set at run time, so it can have a different value for different executions of the program. However, the value of a const field is set to a compile time constant.
Readonly instance fields
- Must have set value, by the time constructor exits
- Are evaluated when instance is created
How to make a class immutable ??
Immutable class is a type of class whose object cant be modified after their creation, which means only constructor will be able to modify or write the fields values of the class.
Java :
In java best way to make a class as immutable is to declare all the fields or variables of the class as final, so declaring final, will prevent the variable or fields to be modified outside the constructor, it will also look after the memory synchronization.
Code Example :
How to check if a link list is circular of is a loop??

This is one of the important question interviewers askes and you are supposed to at least give a logical answer to it, so the logic behind this is to “ Create two markers (pointers) move one pointer faster other slower in a loop, so if these two pointers meets at some point, before the link list ends (while not null) means the link list is circular else if the two pointer meets when the link list ends means while null becomes true means the link list is not circular.
Example Code :
while (SlowPointer) {
SlowPointer = SlowPointer->next;
FastPointer = FastPointer->next;
if (FastPointer) FastPointer=FastPointer->next;
if (SlowPointer == FastPointer) {
print ("circular\n");
}
}
Tuesday, March 27, 2012
Where is pass by reference is useful?
Suppose you have large object to pass to a function, better to pass by reference instead of passing bye value or the object itself.
2.
Least Memory Management.
3.
No 0 values possible -> Called function will know that the object have been created and you are passing address of that object.
4.
New variable are not created, rather already created objects or variable are used.
5.
We can return multiple values from a function.
6.
It allows us to have the function change the value of the argument, which is sometimes useful.
7.
more practical reason will come soon ......
Thursday, March 1, 2012
Difference between ref and out parameters in .NET
 The out Parameter
The out ParameterSunday, February 5, 2012
Disscuss access specifier in c#

Saturday, February 4, 2012
Write a code to get file name from file path in c#
String filePath = @"c:\file\neme\file.txt";
=> filePath.Split('\\')[filePath.Split('\\').Length-1] ----> Will give file name with extension
=> (filePath.Split('\\')[filePath.Split('\\').Length-1]).Split('.')[0] --> Will give file name without extension
=> filePath.Split('\\')[0] --> Will give drive letter
What are Delegates?
A delegate is a form of type-safe function pointer used by the .NET Framework. Delegates specify a method to call and optionally an object to call the method on. They are used, among other things, to implement callbacks and event listeners. It encapsulates a reference of a method inside a delegate object. The delegate object can then be passed to code which can call the referenced method, without having to know at compile time which method will be invoked.
How a thread is created ?
In Detail :
1. Create a System.Threading.Thread
object.2. Create the call back function
3. Starting the Thread
/ \ / \
| (1) | (2)
newThread.Start()
/ \
| (3)

What is thread join?
Syntax of this method :
// create a new thread object from thread class
Thread threadToJoin = new Thread(threadmethod);
//Thread have come to running state.
threadToJoin.Start();
// Wait for foreground thread to end.
threadToJoin.Join()
^
| ____ so this threadToJoin thread will wait, until other threads are terminated.
void threadmethod()
{
//method body
}

Tuesday, January 24, 2012
What’s the advantage of using System.Text.StringBuilder over System.String?
What is an ABC?
What is a "virtual constructor"?
public:
virtual ~Shape() { } // A virtual destructor
virtual void draw() = 0; // A pure virtual function
virtual void move() = 0;
...
virtual Shape* clone() const = 0; // Uses the copy constructor
virtual Shape* create() const = 0; // Uses the default constructor
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
Circle* clone() const; // Covariant Return Types; see below
Circle* create() const; // Covariant Return Types; see below
...
};
Circle* Circle::clone() const { return new Circle(*this); }
Circle* Circle::create() const { return new Circle(); }
When should my destructor be virtual?
- if someone will derive from your class,
- and if someone will say
new Derived , where Derived is derived from your class, - and if someone will say
delete p , where the actual object's type is Derived but the pointer p's type is your class.
How can a member function in my derived class call the same function from its base class?
{
p->goBowling(); ← pretend
}
{
__Fred__goBowling(p); ← pseudo-code only; not real
}
What happens in the hardware when I call a virtual function? How many layers of indirection are there? How much overhead is there?
class Base {
public:
virtual arbitrary_return_type virt0(...arbitrary params...);
virtual arbitrary_return_type virt1(...arbitrary params...);
virtual arbitrary_return_type virt2(...arbitrary params...);
virtual arbitrary_return_type virt3(...arbitrary params...);
virtual arbitrary_return_type virt4(...arbitrary params...);
...
};
What's the difference between how virtual and non-virtual member functions are called?
How can C++ achieve dynamic binding yet also static typing?
What is a "virtual member function"?
What is the difference betweein pointer to constant or a constant pointer?
We have :
char *const p1="Shashwat";
char const* p2="Shriparv";
How do I call a C++ function from C?
// C++ code:
extern "C" void f(int);
void f(int i)
{
// ...
}
Now f() can be used like this:
/* C code: */
void f(int);
void cc(int i)
{
f(i);
/* ... */
}
Why can't I overload dot, ::, sizeof, etc.?
. (dot) :: ?: sizeofThere is no fundamental reason to disallow overloading of ?:. I just didn't see the need to introduce the special case of overloading a ternary operator. Note that a function overloading expr1?expr2:expr3 would not be able to guarantee that only one of expr2 and expr3 was executed. Sizeof cannot be overloaded because built-in operations, such as incrementing a pointer into an array implicitly depends on it. Consider:
X a[10]; X* p = &a[3]; X* q = &a[3]; p++; // p points to a[4] // thus the integer value of p must be // sizeof(X) larger than the integer value of q
What is the difference between new and malloc()?
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
Cicle(Point c, int r);
// no default constructor
// ...
};
What's the value of i++ + i++?
v[i] = i++;Related example:
f(v[i],i++);Here, the result is undefined because the order of evaluation of function arguments are undefined. Having the order of evaluation undefined is claimed to yield better performing code. Compilers could warn about such examples, which are typically subtle bugs (or potential subtle bugs). I'm disappointed that after decades, most compilers still don't warn, leaving that job to specialized, separate, and underused tools.
Thursday, January 19, 2012
How to: Add a Content Type to a SharePoint List using C#
Create a SharePoint 2010 Project
In this task, you create an empty SharePoint 2010 project in Microsoft Visual Studio 2010.To create the SharePoint project
- To start Visual Studio 2010, click the Start Menu, click All Programs, click Microsoft Visual Studio 2010, and then click Microsoft Visual Studio 2010.
- On the File menu, point to New, and then click Project.
- In the New Project dialog window, in the Installed Templates section, click Visual C#, click SharePoint, and then click2010.
- Select Empty SharePoint Project from the project items.
- In the Name box, type CreateContentType and then click OK.
- In the SharePoint Customization Wizard, type the local Web site that you want to use for this exercise (such as http://localhost/SampleWebSite).
- For the trust level, select Deploy as a farm solution and then click Finish.
Create a Content Type
Monday, January 16, 2012
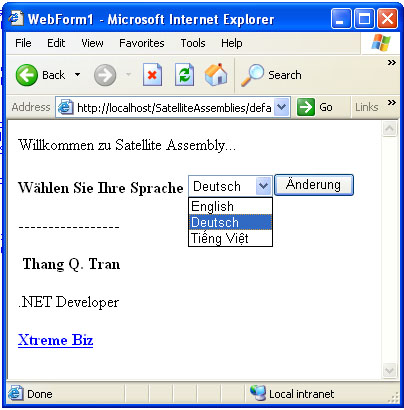
What are Satellite Assemblies?
Tell Something about class/object life cycle...

- Load the assembly
- Execute static initialisers
- "new" call:
- allocate memory
- execute non-static initialisers
- execute constructor
- the instance is now ready to be used
- after the last reference to the object has vanished: if the object has no finalizer, it is now ready for collection; if the object has a finalizer, it is put on the finalizer queue.
- (optional) the objects from the finalizer queue have their finalizer called in a special thread; if there is still no reference from the application to the object, it too becomes now eligible for garbage collection
- the garbage collector deallocates memory
Sunday, January 15, 2012
What is Singleton Class in C++?
- Application classes. There should only be one application class.
- Logger classes. For logging purposes of an application there is usually one logger instance required.
Saturday, January 14, 2012
What is difference between dot net framework 3.5 and 4.0?
Tell something about View State in Asp.Net
As we know A Web application is stateless. A new instance of the Web page class is created every time that the page is requested from the server. This would ordinarily mean that all information in the page and in its controls would be lost with each round trip. For example, by default if a user enters information into a text box on an HTML Web page, that information is sent to the server. However, it is not returned to the browser in the response.
To overcome this intrinsic limitation of Web programming, the ASP.NET page framework includes several state-management features to preserve page and control values between round trips to the Web server.
What is post back in Asp.Net
When to use Abstract Class and when to use Interface in project?